Outline of the Article1. Introduction
- Definition of Air Pollution
- The Growing Concern Over Air Pollution
2. What Causes Air Pollution?
- Natural Sources
- Human-Induced Sources
3. The Different Types of Air Pollutants
- Particulate Matter (PM)
- Nitrogen Oxides (NOx)
- Sulfur Dioxide (SO2)
- Carbon Monoxide (CO)
- Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs)
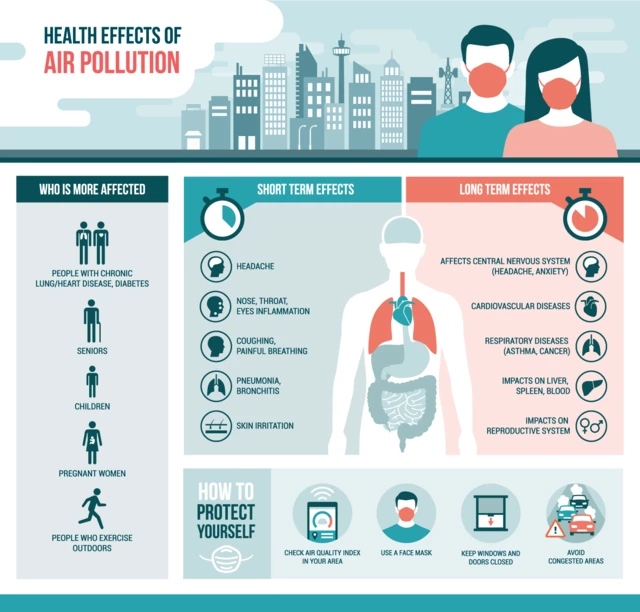
4. Short-Term Effects of Air Pollution on Human Health
- Respiratory Issues
- Eye Irritation
- Fatigue and Headaches
5. Long-Term Effects of Air Pollution on Human Health
- Chronic Respiratory Diseases
- Cardiovascular Problems
- Cancer Risks
- Impact on the Nervous System
6. Vulnerable Populations
- Children
- Elderly
- People with Pre-existing Health Conditions
7. The Role of Air Pollution in Allergies and Asthma
- How Air Pollutants Trigger Allergies
- Asthma and the Air Pollution Link
8. Air Pollution’s Effect on Mental Health
- Increased Stress and Anxiety
- Cognitive Decline
9. Impact of Air Pollution on Pregnancy and Child Development
- Risks for Pregnant Women
- Developmental Issues in Children
10. How Air Pollution Affects the Immune System
- Weakening the Immune Response
- Increased Susceptibility to Infections
11. Air Pollution and the Environment
- Impact on Climate Change
- Ecosystem Damage
12. How to Protect Yourself from Air Pollution
- Indoor Air Quality
- Wearing Masks
- Limiting Outdoor Exposure
13. The Importance of Government Action and Policies
- Air Quality Standards
- Technological Innovations
- Urban Planning Solutions
14. What You Can Do to Help Combat Air Pollution
- Reducing Car Usage
- Supporting Clean Energy
- Planting Trees
15. Conclusion
- Recap of Air Pollution's Effects
- Call to Action for a Healthier Environment
Air pollution is one of the most pressing environmental challenges today. It refers to the presence of harmful substances in the air that can affect the health of humans, animals, and ecosystems. With industrialization, increased vehicle emissions, and other human activities, air pollution has become a serious global concern. The effects of air pollution on human health are widespread and vary from short-term irritations to long-lasting diseases. Let’s dive deeper into how air pollution is harming our bodies and what we can do about it.
What Causes Air Pollution?
Understanding the root causes of air pollution is key to tackling it.
Natural Sources
Some air pollution is naturally occurring. Forest fires, volcanic eruptions, and dust storms can release large amounts of particulate matter and gases into the atmosphere. While natural sources play a part, the major contributor to the air pollution we face today is human activity.
Human-Induced Sources
The burning of fossil fuels for energy, vehicle emissions, industrial activities, and agricultural practices are primary contributors to air pollution. Factories, power plants, and car exhausts release harmful chemicals into the air, which have serious consequences for both the environment and human health.
The Different Types of Air Pollutants
Air pollutants come in various forms, each with its unique effect on human health.
Particulate Matter (PM)
These are tiny particles suspended in the air, such as dust, soot, and smoke. PM2.5 (particles with a diameter of 2.5 micrometers or less) is particularly dangerous as it can penetrate deep into the lungs and bloodstream.
Nitrogen Oxides (NOx)
Mainly produced by vehicles and power plants, NOx contributes to the formation of ground-level ozone and acid rain, both harmful to human health.
Sulfur Dioxide (SO2)
SO2 is released primarily from the burning of coal and oil. This pollutant can irritate the lungs and aggravate existing respiratory conditions like asthma.
Carbon Monoxide (CO)
Produced by vehicle exhaust and industrial processes, CO can interfere with oxygen delivery in the body, leading to fatigue, chest pain, and even death in high concentrations.
Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs)
These chemicals are found in paints, solvents, and other industrial products. VOCs can contribute to the formation of ground-level ozone, which worsens respiratory issues.
Short-Term Effects of Air Pollution on Human Health
When you’re exposed to air pollution, even for a short period, it can lead to several immediate health effects.
Respiratory Issues
The inhalation of polluted air can cause a range of respiratory problems. Coughing, shortness of breath, and chest tightness are common symptoms. People with asthma may experience more frequent attacks.
Eye Irritation
Polluted air, particularly with high levels of particulate matter, can irritate the eyes, causing redness, dryness, and discomfort.
Fatigue and Headaches
Air pollution can also lead to fatigue and headaches. This is often due to the reduced oxygen levels in polluted air, which can affect brain function and make you feel sluggish or dizzy.
Long-Term Effects of Air Pollution on Human Health
Long-term exposure to air pollution can have severe consequences for health.
Chronic Respiratory Diseases
Prolonged exposure to pollutants like PM2.5 can lead to chronic conditions such as chronic bronchitis and emphysema. These diseases limit airflow and reduce lung function, making breathing difficult.
Cardiovascular Problems
Air pollution has been linked to heart disease. Particulate matter can cause inflammation in the blood vessels, increasing the risk of heart attacks and strokes.
Cancer Risks
Certain pollutants, such as benzene and formaldehyde, are classified as carcinogens. Long-term exposure increases the risk of lung cancer and other cancers of the respiratory system.
Impact on the Nervous System
Studies show that air pollution can damage the nervous system. It can impair cognitive function, leading to a decline in memory and concentration.
Vulnerable Populations
Certain groups of people are more susceptible to the harmful effects of air pollution.
Children
Children breathe in more air relative to their body weight than adults, making them more vulnerable to the effects of polluted air. They may experience developmental issues and lung damage.
Elderly
Older adults are more likely to suffer from chronic conditions like heart disease or lung disease, which are aggravated by exposure to air pollution.
People with Pre-existing Health Conditions
Individuals with asthma, COPD, and other respiratory or cardiovascular conditions are at higher risk of severe health impacts from air pollution.
The Role of Air Pollution in Allergies and Asthma
Air pollution is a major trigger for allergies and asthma.
How Air Pollutants Trigger Allergies
Pollutants such as ozone and particulate matter can irritate the respiratory system, making allergic reactions worse. Common symptoms include sneezing, congestion, and itching.
Asthma and the Air Pollution Link
Asthma sufferers are particularly sensitive to pollutants. Exposure can cause asthma attacks, wheezing, and difficulty breathing.
Air Pollution’s Effect on Mental Health
Recent studies suggest that air pollution also affects mental health.
Increased Stress and Anxiety
Pollution-induced air quality deterioration can cause anxiety, stress, and sleep disturbances. People living in highly polluted areas often report higher levels of mental distress.
Cognitive Decline
Long-term exposure to air pollution has been linked to cognitive decline, especially in elderly populations. Studies suggest that pollutants may affect brain health, leading to issues like dementia and Alzheimer's.
Impact of Air Pollution on Pregnancy and Child Development
Pregnant women exposed to high levels of air pollution are at risk of complications.
Risks for Pregnant Women
Air pollution can increase the likelihood of pregnancy complications, including preterm birth and low birth weight.
Developmental Issues in Children
Children exposed to polluted air may experience developmental delays and lower IQ scores. They are also more likely to develop asthma and other respiratory problems.
How Air Pollution Affects the Immune System
Air pollution doesn’t just harm the lungs – it can also weaken the immune system.
Weakening the Immune Response
Air pollutants like particulate matter and VOCs can interfere with immune function, making the body more susceptible to infections and diseases.
Increased Susceptibility to Infections
Individuals exposed to high levels of pollution are more vulnerable to respiratory infections, including pneumonia and bronchitis.
Air Pollution and the Environment
The effects of air pollution extend beyond human health.
Impact on Climate Change
Pollutants like carbon dioxide and methane contribute to global warming. This accelerates climate change, causing extreme weather events and rising sea levels.
Ecosystem Damage
Air pollution also harms ecosystems. Acid rain, a result of pollutants like sulfur dioxide, damages plants, aquatic life, and soil health.
How to Protect Yourself from Air Pollution
There are steps you can take to reduce your exposure to air pollution.
Indoor Air Quality
Ensure your home has proper ventilation and air filtration systems. Using air purifiers and keeping windows closed during high pollution times can help.
Wearing Masks
Wearing N95 masks can reduce the inhalation of harmful particles in polluted areas.
Limiting Outdoor Exposure
Stay indoors during peak pollution hours. Limit outdoor physical activity in areas with poor air quality.
The Importance of Government Action and Policies
Governments play a crucial role in reducing air pollution.
Air Quality Standards
Setting strict air quality standards and enforcing regulations for emissions can help limit pollution levels.
Technological Innovations
Investing in clean energy technologies and improving industrial processes can reduce harmful emissions.
Urban Planning Solutions
Urban planning that promotes green spaces, public transport, and clean infrastructure can help improve air quality in cities.
What You Can Do to Help Combat Air Pollution
Every individual has a role to play in tackling air pollution.
Reducing Car Usage
Walk, cycle, or use public transport instead of driving. This reduces carbon emissions and traffic congestion.
Supporting Clean Energy
Switch to renewable energy sources like solar or wind. This reduces reliance on fossil fuels and cuts emissions.
Planting Trees
Trees absorb carbon dioxide and improve air quality. Planting trees in urban areas can help mitigate pollution.
Conclusion
Air pollution is a serious threat to human health and the environment. Its effects range from short-term respiratory irritation to long-term diseases like cancer and cardiovascular problems. Vulnerable populations such as children and the elderly are especially at risk. While we cannot control natural sources of pollution, reducing human-induced pollution through cleaner technologies, policies, and personal choices is crucial. By acting together, we can ensure a healthier future for ourselves and the planet.
-
What are the main causes of air pollution?
Air pollution is caused by both natural and human activities, with industrial emissions, vehicle exhaust, and agricultural practices being the primary contributors. -
How does air pollution affect children?
Children are more susceptible to air pollution, experiencing respiratory issues, developmental delays, and increased risk of asthma. -
Can air pollution cause cancer?
Yes, long-term exposure to certain air pollutants, such as benzene, formaldehyde, and radon, can increase the risk of lung cancer and other cancers. -
What can I do to protect myself from air pollution?
You can protect yourself by staying indoors during high pollution days, using air purifiers, wearing masks, and reducing your outdoor activity. -
How does air pollution impact mental health?
Air pollution has been linked to increased stress, anxiety, and cognitive decline, particularly in older adults.